|
|
|
Configuration |
|
Material Specification |
|
Working Pressure |
|
Size |
|
Connection Type |
|
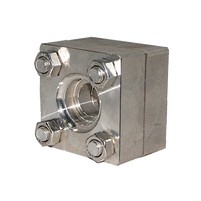
Square flanges are flanges made for the connection of hydraulic systems to another component. They are produced following the B2291 / JIS F7806 standards. They are also used for a pipe to pipe connection, especially where the pipes are made of steel and stainless steel materials. Just as the name, square flanges have a square shape.
Even though the square flanges are in JIS standards, they are also produced in other standards as the country’s law and different pressure ratings to help them serve diverse purposes. The standard size for these flanges ranges between 1/4” to 6”. The square flange has three configurations - SHAB, SSAB, KAB, LSA, and Square Blind Flange.
Even though the square flanges are in JIS standards, they are also produced in other standards as the country’s law and different pressure ratings to help them serve diverse purposes. The standard size for these flanges ranges between 1/4” to 6”. The square flange has three configurations - SHAB, SSAB, KAB, LSA, and Square Blind Flange.
1. What is Square Flange?
|
Square flanges are connecting tools that join nominal bore pipe sizes to another. It is also used for connecting between pipe to other components like valves, elbows, and tees. They are made following the JIS B2291 standards and have a working pressure between 210kg/cm² to 350kg/cm². They can be used with high-pressure hydraulic systems with 3000 PSI working pressure. This standard also makes square flanges suitable to work with pipes made with these standards.
Systems that use stainless steel and steel pipes need square flanges to have a seamless flow of liquids throughout the system. Although they are produced in sizes from 1/4 inches to 6 inches, the popular sizes used are 1/2 inches to 2 inches. The three types of square flanges are SHAB, KAB, and SSAB. They are commonly used for steam lines and oil systems in hydraulics. |
2. What is Square Flange material?
Square flanges are made from two materials – Stainless steel (SS316) and steel (SF440A). Stainless steel (SS316) is a preferred material for many industrial tools because of its benefits. Generally, corrosion is a problem that affects lots of metal tools. This corrosion problem is caused by a host of environmental changes, chemical contact, etc. Due to this, there needed to be a unique material that is resistant to some of these factors to elongate the products' lifespan. Stainless steel flanges have an overall advantage over other flanges because of its high corrosion resistance property. SS316 is very strong, able to withstand high pressures and temperatures, and lasts longer.
Steel (SF440A) is known as carbon steel and it is one of the most primitive steel types used in manufacturing tools. SF440A is a Japanese forged steel standard defined in JISG3201-88. Carbon steel flanges have extra hardness and strength which plays out during production. Also, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and durability are another strong point for carbon steel flanges. SF440A contains carbon content within 0.05% to 2.1%.
Steel (SF440A) is known as carbon steel and it is one of the most primitive steel types used in manufacturing tools. SF440A is a Japanese forged steel standard defined in JISG3201-88. Carbon steel flanges have extra hardness and strength which plays out during production. Also, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and durability are another strong point for carbon steel flanges. SF440A contains carbon content within 0.05% to 2.1%.
Grade |
P (%) |
Fe (%) |
C (%) |
S (%) |
Si (%) |
SF440A: Minimum |
- |
99.25 |
- |
- |
- |
SF440A: Maximum |
0.040 |
100 |
0.26 |
0.050 |
0.4 |
The table inserted above shows the chemical composition of SF440A flanges.
Grade |
Yield Strength minimum (MPa) |
Elongation minimum % |
Tensile Strength (MPa) |
SF440A |
Thickness ≥ 16mm: 235 Thickness ˂ 16mm: 245 |
Thickness ˂ 5mm: 21 Thickness ˂ 5 -16mm: 17 Thickness ≥16mm: 21 |
400 - 510 |
The table above shows the Mechanical Composition of Carbon steel.
Properties |
Imperial |
Metric |
Thermal Expansion Coefficient (@0-100⁰C/32-212⁰F) |
- |
11 m/mK |
Thermal Conductivity |
20 BTU in/hr.ft.⁰F |
50W/mK |
This table shows the thermal expansion of the carbon steel.
Carbon steel flanges have extra hardness and strength which plays out during production. Also, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, and durability are another strong point for carbon steel flanges.
3. How many types of pipe Square Flanges are there?
|
While trying to identify a flange, there is a list of factors to guide you. And the right flange must be used because a wrong flange will affect the application’s effectiveness and other damages might occur. Therefore, to identify flange, consider these factors:
Type of Flange: Flanges have a unique way they look. This is called the face of the flange. These faces can either be tongue and groove, flat face, socket weld, weld neck, or threaded bore. For a square flange, it uses the socket weld or the weld-in face. Flange Size: The size of the flange is made following standards, working pressure level, and measurements of the flange. The square flange is made with the JIS B2291 and JIS F7806 standards. They can withstand a high-pressure level and the pressure scales are 210kg/cm², 280kg/cm², and 350kg/cm². The flanges are made in sizes from 1/4 inches to 6 inches. |
The configurations complete set for square flanges are SHAB, SSAB, LSA, KAB, and Blind flange.
The standard complete set of a square flange comes with 5 components. 1 male flange (flat side) labelled as B, 4 hexagon or Allan cap screws, 4 hexagon nuts (optional), 1 female flange (O-ring side) named as the A-side, and an NBR 70/90 O-ring. Hexagon bolts and nuts are used for the tightening of the sides of the flanges. While SSAB flange design comes with bolt thread at the flat side, it does not require nut in the installation.
- The SHAB works with a pressure of 210kg/cm². It is attached to hexagon bolts and nuts. Also, it is the most used square flange configuration in industries.
- SSAB has a working pressure of 210kg/cm² also. But, it has a smaller body when compared to the SHAB. For application, it is combined with a socket cap screw.
- KAB series is similar in configuration to SHAB series, however, the difference in the working pressure. The working pressure for the KAB series is 280kg/cm² and 350kg/cm². Also, they are used with hexagon bolts and nuts.
- The LSA is a type of O-ring side specially designed, and the flow of fluids is L-shaped internally.
- Square Blind Flanges are designed to seal the end of pipes to prevent oil leakage.
The standard complete set of a square flange comes with 5 components. 1 male flange (flat side) labelled as B, 4 hexagon or Allan cap screws, 4 hexagon nuts (optional), 1 female flange (O-ring side) named as the A-side, and an NBR 70/90 O-ring. Hexagon bolts and nuts are used for the tightening of the sides of the flanges. While SSAB flange design comes with bolt thread at the flat side, it does not require nut in the installation.
4. Why Square Flange are used in piping?
|
Square flanges are important in industries working with high-pressure machines. they are used for a pipe to pipe connections and connection of pipes to other components. Generally, it is used as a tool for pipe fittings. However, the square flanges are not recommended for large diameter pipes and high torque environments. Instead, small diameter pipes are suitable to be used alongside square flanges. Square flanges are necessary for these industries:
|
5. How can you attach Square Flanges to Pipes and other components?
Installing a square flange requires your understanding and mastering the installation procedures coupled with the right sizes for bolts, nuts, and torque. These following steps will illustrate how to assemble square flanges quickly and simply:
STEP 1
The first step in installing any flange type is ensuring the surface area is contamination and scratch-free. These two factors can cause damage to the flange or leakage of fluids to the wrong parts of the hydraulic system, therefore, you have to follow the instruction. After cleaning thoroughly, apply lubricants on the O-ring parts.
STEP 2
Position the flanges at the right spots, well-aligned, and then place the bolts in their holes.
STEP 3
Using your hand, tighten the bolts and nuts to hold the flange firmly. Ensure you do not over tighten the nuts.
STEP 4
You can use a wrench to ensure the ultimate tightness is achieved.
STEP 1
The first step in installing any flange type is ensuring the surface area is contamination and scratch-free. These two factors can cause damage to the flange or leakage of fluids to the wrong parts of the hydraulic system, therefore, you have to follow the instruction. After cleaning thoroughly, apply lubricants on the O-ring parts.
STEP 2
Position the flanges at the right spots, well-aligned, and then place the bolts in their holes.
STEP 3
Using your hand, tighten the bolts and nuts to hold the flange firmly. Ensure you do not over tighten the nuts.
STEP 4
You can use a wrench to ensure the ultimate tightness is achieved.
6. How to purchase Square Flange with Impa Code?
|
Impa code stands for International Marine Purchasing Association and it is a world’s leading reference source in the marine industry for maritime procure, purchasing and supply. Impa code is formed to provide a universal coding system to facilitate communication between ship engineer and marine suppliers.
The square flange impa code is the common description for the vessel to purchase the correct part. Please refer to the full list of square flange SHA and SHB Impa Code below: |
Size (DN) |
Size (inch) |
Impa Code |
Model |
Description |
Working Pressure |
15A |
1/2" |
734801 |
SHA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
20A |
3/4" |
734802 |
SHA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
25A |
1" |
734803 |
SHA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
32A |
1 1/4" |
734804 |
SHA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
40A |
1 1/2" |
734805 |
SHA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
50A |
2" |
734806 |
SHA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
65A |
2 1/2" |
734807 |
SHA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
80A |
3" |
734808 |
SHA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
15A |
1/2" |
734811 |
SHB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
20A |
3/4" |
734812 |
SHB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
25A |
1" |
734813 |
SHB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
32A |
1 1/4" |
734814 |
SHB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
40A |
1 1/2" |
734815 |
SHB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
50A |
2" |
734816 |
SHB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
65A |
2 1/2" |
734817 |
SHB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
80A |
3" |
734818 |
SHB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
Please refer to full list of square flange SSA and SSB Impa Code below:
Size (DN) |
Size (inch) |
Impa Code |
Model |
Description |
Working Pressure |
15A |
1/2" |
734821 |
SSA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
20A |
3/4" |
734822 |
SSA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
25A |
1" |
734823 |
SSA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
32A |
1 1/4" |
734824 |
SSA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
40A |
1 1/2" |
734825 |
SSA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
50A |
2" |
734826 |
SSA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
65A |
2 1/2" |
734827 |
SSA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
80A |
3" |
734828 |
SSA |
O-ring Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
15A |
1/2" |
734831 |
SSB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
20A |
3/4" |
734832 |
SSB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
25A |
1" |
734833 |
SSB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
32A |
1 1/4" |
734834 |
SSB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
40A |
1 1/2" |
734835 |
SSB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
50A |
2" |
734836 |
SSB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
65A |
2 1/2" |
734837 |
SSB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
80A |
3" |
734838 |
SSB |
Flat Side |
210 KGF/CM2 |
square flanges catalogue