|
|
|
Material Specification |
|
Connection Type |
|
Size |
|
Working Pressure |
|
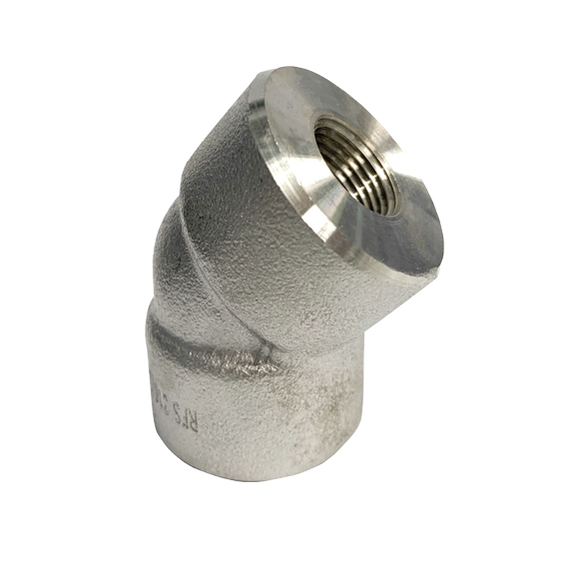
Forged Pipe Fittings are connectors placed between nominal bore pipes. They are made following the ASME B16.11, BS3799, and MSS-SP-79/83/95/97. The name ‘Forged Pipe’ is given from the manufacturing process of the pipe fitting. The forged pipe fittings are made from stainless steel SS316 and carbon steel A105 materials.
Both-well from Taiwan is the brand that is available in stock. Furthermore, they are available in a variety of sizes ranging from 1/8” to 4”. The working pressure for the forged pipe fitting is 3000 PSI and 6000 PSI. The connection types for this pipe fitting is NPT / BSPP (threaded) or socket weld (Weld in). There has to be a suitability feature between the two components to connect the fittings to the pipe ends. Other connection types can be available upon request.
Both-well from Taiwan is the brand that is available in stock. Furthermore, they are available in a variety of sizes ranging from 1/8” to 4”. The working pressure for the forged pipe fitting is 3000 PSI and 6000 PSI. The connection types for this pipe fitting is NPT / BSPP (threaded) or socket weld (Weld in). There has to be a suitability feature between the two components to connect the fittings to the pipe ends. Other connection types can be available upon request.
|
|
STUDY CATALOGUE HERE |
|
1. What are Forged Pipe Fittings?
|
Forged Pipe Fittings are fittings manufactured from forged steel materials. They are made to fulfill the standards of ASME B16.11, MSS-SP-79/83/95/97, and BS3799. They are used as a connecting device for nominal bore, pipes, and pipelines. The forging process creates a finished product with high strength, resistance to climatic conditions, and highly durability.
ASME B16.11 is a standard developed for forged steel fittings. The standard gives a set of specifications such as material (carbon steel, stainless steel), connection type (socket weld and threaded), and classification into 2000, 3000, 6000 or 9000. The threaded end fittings are under the class 2000, 3000, and 6000, while socket weld fittings are under class 3000, 6000, and 9000. It further states other specifications like pressure and temperature ratings, tolerances and so on. |
2. What are Forged Pipe Fittings made of?
Forged pipe fittings are made from two materials – Carbon Steel (ASTM A105) and Stainless Steel (ASTM A182). The carbon steel fitting surface can also pass through a galvanization process to increase its corrosion resistance. This service can be available upon request.
A forged pipe fitting is recommended because it has high strength, high quality, and can withstand a high level of pressure. Also, the wall thickness has been increased to be more than other pipe fittings used for threading or socket weld ends. More so, the ASME B16.11 standards have ratings for pressure and temperature, tolerances, requirements for materials, dimensions, and markings. Forged Pipe Fittings are applied in various industries where chemicals, liquids, gases, and other fluid types are used, especially where fittings are exposed to corrosion and high pressure.
A forged pipe fitting is recommended because it has high strength, high quality, and can withstand a high level of pressure. Also, the wall thickness has been increased to be more than other pipe fittings used for threading or socket weld ends. More so, the ASME B16.11 standards have ratings for pressure and temperature, tolerances, requirements for materials, dimensions, and markings. Forged Pipe Fittings are applied in various industries where chemicals, liquids, gases, and other fluid types are used, especially where fittings are exposed to corrosion and high pressure.
3. How are Forged Pipe Fittings made?
|
The forging process is one of the manufacturing methods of shaping metal into the desired form by using local compressive tools. The forging process is based on the type of method used. There are cold forging, warm forging, and hot forging. For the production of forged pipe fittings, the material is exposed to heat to allow melting to occur, thereafter, the heated steel is formed into forged fittings. These materials are durable, provide tight sealing and reduced leakages for piping systems.
The class pressure falls between 3000 PSI and 6000 PSI, and they are represented as 3M or 6M. 1M here represents 1000, therefore, 3M means 3000 lbs fittings, that is, the fitting can work with a maximum of 3000 PSI or 206 Bars for working pressure.
The carbon steel (A105) material is unmarked because it is classified as a standard material grade. However, other materials like stainless steel are marked on the body in open areas. |
The fittings are stamped with permanent markings of identification on the collar portion. This is done to simplify users' identification process to enable perfect installation and effective working of the system. The various markings include:
|
4. What does 3M mean on Forged Pipe Fittings?
|
The pressure of forged pipe fittings falls between these numbers:
|
Of these four numbers, the standard forged pipe fittings are designed with the pressure that falls between class 3000 and 6000. Please refer to the table below for the difference between 3M and 6M pipe fittings:
|
5. How many types of Forged Pipe Fittings are there?
|
There’s a wide list of forged pipe fittings to select from for customization. They include straight coupling, end plug, hex nipple, 3 piece union, 90D elbow, 3-way tee, end cap, 45D elbow, and many more.
The 3-way tee forged pipe fitting is designed in a T-shape with one inlet and two outlets. It is used for systems that operate with one inlet and two outlets. The reducer fittings is a tool used to minimize the flow size from a larger flow to a smaller flow, while the Hex Bush fitting is used to increase the flow from a smaller to a larger one. |
The table below shows the different types of fitting and suitable connection types:
|
6. How much pressure can a Forged Pipe Fittings hold?
For forged pipe fittings, the connection types are either threaded or socket weld end. The threaded end can either be NPT or BSPP, however, the NPT thread is the renowned type because it gives a better sealing during installation. The female and male threads compress, threads and wedges together. The BSP parallel thread can also be used for other connections such as hex nipple, full coupling, and hex plug.
As an alternative method, welding can also be used to attach pipes and fittings. The pipe with the plain end is inserted into a hollow area of fittings before the welding process begins. All standard fittings use similar connection types, but it can be customized upon request for systems with special connection types.
After the fitting connects to the pipe, the schedule pipe corresponds to each class pressure of fittings and the materials all combined to ensure the system's efficient functioning.
The table below shows the pipe schedule thickness:
As an alternative method, welding can also be used to attach pipes and fittings. The pipe with the plain end is inserted into a hollow area of fittings before the welding process begins. All standard fittings use similar connection types, but it can be customized upon request for systems with special connection types.
After the fitting connects to the pipe, the schedule pipe corresponds to each class pressure of fittings and the materials all combined to ensure the system's efficient functioning.
The table below shows the pipe schedule thickness:
To calculate the minimum pipe wall thickness, factors like application pressure design and others like environment factor, corrosion, threaded depth, and surrounding temperature.
FORGED PIPE FITTINGS CATALOGUE