|
|
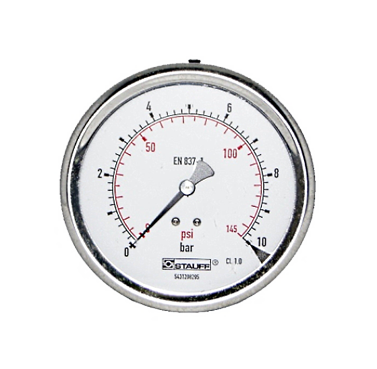
Pressure gauges are basic instruments designed to measure the level of pressure rating in systems. Pressure gauges are used for copper-based alloys systems for liquid and gaseous applications. The general Stauff pressure gauges are produced in line with the European Standard EN 837-1. Pressure gauges are available in two different types which are analog pressure gauge and digital pressure gauge. These gauges are applied in systems for measuring the level of performance and efficiency and to ensure the smooth running of the systems. Pressure gauges are available in sizes ranging from 2 1/2” and 4”. They are made from stainless steel and brass and able to withstand a maximum working pressure of 700 bars. Pressure readings are measured in PSI (pounds per square inch) and Bar (kilopascal). |
Material Specification |
|
Pressure Reading |
|
Size |
|
Working Pressure |
|
1. What is a Pressure Gauge used for?
|
Pressure gauges are instruments used to measure the rate of pressure in systems. Measuring pressure in machines is an important activity. Many industries using mechanical devices engage in measuring the level of pressure used by the machines. This helps to ascertain the level of performance and efficiency of the machines. There are various equipment used to measure the pressure level in devices such as pressure gauges.
Pressure gauges show the gauge pressure when used for measurement. Gauge pressure is the differential in two pressures. Pressure gauges are either portable or installed as a stationary tool for calculating the pressure rating in hydraulic systems. They are available in various connection port types to ensure the flexibility of the device and suitability with different machines. Also, pressure readings are available in different ranges. |
2. What is the working principle of Pressure Gauge?
The table below shows the major specifications of the analogue and digital pressure gauges:
Dial Size in inch |
|
|
Dial Size in mm |
|
|
Size connection |
|
|
Connection |
|
|
Thread connection |
|
|
The dial faces of the gauge in a size range of 63MM (2 1/2”) and 100MM (4”). Also, the connection ends are in two types, panel (back) mounting and stem (bottom) mounting while the thread connection is in NPT (1/4”NPT and 1/2”NPT) and BSPP (G1/4” and G1/2”). This is used to join systems working with nominal size as the major measurement. For nominal size systems using 1/2 inches, the dial face measurement is 100MM, while a nominal size system using 1/4 inches will use a dial face measurement of 63MM.
There are various types of pressure gauges, however, the most commonly used gauge is called the bourdon tube pressure gauge. Bourdon tube gauge works with the average of mechanical movement value. The bourdon tube is a curved tube with a C-shape which allows transmission of pressure internally.
When the substance flows inside the gauge, the inner area of the bourdon tube is exposed to pressure which results in an enlargement of the tube. After that, a conversion of the mechanical movement occurs and the enlargement of the bourdon tube sparks the pinion rotation and causes a revolving movement of the pointer. This will then reveal the current pressure reading of the system on the dial of the gauge.
There are various types of pressure gauges, however, the most commonly used gauge is called the bourdon tube pressure gauge. Bourdon tube gauge works with the average of mechanical movement value. The bourdon tube is a curved tube with a C-shape which allows transmission of pressure internally.
When the substance flows inside the gauge, the inner area of the bourdon tube is exposed to pressure which results in an enlargement of the tube. After that, a conversion of the mechanical movement occurs and the enlargement of the bourdon tube sparks the pinion rotation and causes a revolving movement of the pointer. This will then reveal the current pressure reading of the system on the dial of the gauge.
3. What are the different types of Pressure Gauges?
Pressure gauges are available in two major types – Analog and Digital pressure gauges.
- Analog pressure gauges are the oldest developed gauges developed over 150 years ago. They were used when the use of the steam process became a common activity in industries. These gauges have dual scales pressure indication measured in PSI (pounds per square inch) or bar. Analog pressure gauges are the most renowned gauges. More so, analog pressure gauges use the mechanical movement principle which makes it easy to use and operate. Moreover, analog pressure gauges are very cost-effective and can operate solely without a power source attached. Pressure reading on this gauge is very easy to read. On the dial of the gauge, there’s a needle that precisely reacts to the pressure rating level calculated by the gauge. This is shown clearly and easily regulated.
- Digital pressure gauges on the other hand are modified and technologically built pressure gauges. These gauges use innovative microprocessors and sensors to show the precise pressure level of a system. Digital gauges are faster and simpler to read. Also, they are suitable for pressure reading in low pressure systems. More so, the component of a digital pressure gauge is less and they can be scheduled to read multiple pressures with results delivered to analyzing devices such as computer systems. They reveal maximum and minimum pressure values and have a precision of 0.5% of the full scale. Many of the digital pressure gauges work with two measurement technologies which are Strain gauge or Piezoelectric. Digital pressure gauges are mostly used for working pressure measurement of hydraulic oils, water, and lubricants. Both digital and analog pressure gauges are packaged in a pressure test kit and can be configured to the pressure reading that is preferred upon request.
4. What type of oil is used in Pressure Gauge?
|
Pressure gauges can be affected by vibration created in systems and this will reduce the performance and quality of readings the gauges will reveal. The gauges being filled with liquid substance is a way to tackle the problem. Most pressure gauges are filled with glycerin oil to reduce the impact of vibration on the device. The glycerin at room temperature in the pressure gauge will give an improved vibration dampening. The glycerin oil can effectively work in temperature levels ranging from -4⁰F to +140⁰F or -20⁰C to +60⁰C. Glycerin oil in analogue pressure gauges allows the device to sustain the precision of the needle reading. It also minimizes the impact of the extreme vibration and oscillation of the gauge reading needle.
The liquid substance can also help keep the inner components of the pressure gauges from damage while acting as a movement lubricant. It increases the consistency and durability of the pressure gauge. The higher the durability level of the pressure gauge helps to reduce the cost for maintenance and repair of the system as a whole. |
5. What is Pressure Gauge calibration?
|
Pressure gauges can be set to ensure all the readings are precise. This is done by carrying out a test on the gauge, thereafter, a successful calibration certificate will be presented to authenticate the preciseness of the pressure gauge.
This calibration test will aid the user to ascertain and sustain the accuracy level of the pressure gauge. When this is done, the quality and effectiveness of the pressure gauges will contribute to the proper functioning of the device. Pressure gauge with calibration certificate is essential for pressure test to show the reading accuracy. |
6. What are the causes of Pressure Gauge failure?
Pressure gauges are commonly reported to fail during operation and this could lead to fluid leakage, fire emissions, and other dangerous occurrences that could pose a threat to life and property. The common causes are listed below:
- Corrosion of different components of the system
- Steam
- Rough handling of the gauge
- Pressure and temperature spikes
- System vibration
- Pulsation
- Clogging
pressure gauges catalogue