|
|
|
Material Specification |
|
Dimension Specification |
|
Outer Diameter Size |
|
Finishing |
|
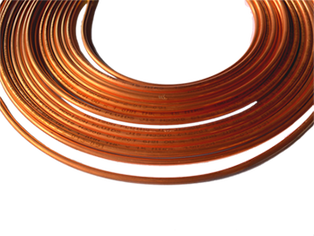
Copper coils are produced in compliance with the Japanese Industrial Standard, JIS H3300. The standard JIS H3300 is used to represent copper alloy and copper seamless tubes and pipes. The rolling up process of the copper coils produce a pancake-like structure, therefore, the coil is given the name pancake copper coil. Copper coils are very durable and reliable, therefore, it is a preferred option for use in several instances. Copper coils can be used in gas lines, solar heating devices, fuel oil systems, water distribution systems, etc. copper coils can serve as transmission channels for liquids, air to cool down the engine of various equipment.
The size range of copper coil is between 6mm to 15mm, and in inches, it ranges from 1/4” to 3/4”. Measurement of external diameter size and thickness of the material's wall is calculated using a wide range based on the product specifications. Copper coils are ideally known to be light-weighted, durable, rust-resistant, have high thermal conductivity, and strong.
The size range of copper coil is between 6mm to 15mm, and in inches, it ranges from 1/4” to 3/4”. Measurement of external diameter size and thickness of the material's wall is calculated using a wide range based on the product specifications. Copper coils are ideally known to be light-weighted, durable, rust-resistant, have high thermal conductivity, and strong.
1. What are Copper Coils?
Copper is an element that is very renowned in the world today. Since the ages past, the element has been put to great use by humans. In the Middle East, copper is among the first sets of metal discovered in the area around 5100 B.C. Also, the United States currency (penny) was made from undiluted copper before it was changed to 97.5% zinc. According to the United States Geological Survey (USGS), copper is classified as the third-most consumed metal globally. Also, copper is a unique element on the periodic table with no natural silver or gray color. It is often used in the production of wires, cables, and other electronic devices.
|
Below is a summary showing the chemical description of copper:
|
Copper coils are produced from the copper metal and are often used in plumbing or production of heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) devices. Asides its high durability, copper coils are a good conductor of heat and suitable in the oil and gas industry.
Above is a table showing the characteristics of copper coils.
|
2. What are Copper Coils used for?
The copper coil is finished with phosphorus deoxidized. During this process, the addition phosphorus is put into the metal for deoxidization. After this, the oxygen content is removed, and the metal has an increased weld-ability. Furthermore, copper coils have weather and corrosion resistance, flexibility, and good conductivity of electricity.
Alloy Grade No C1220T |
Min. |
Max. |
Chemical Composition on (%) Phosphorus (P) |
0.015 |
0.040 |
Chemical Composition on (%) Copper (Cu) |
99.90 |
- |
The table above shows the chemical composition for C1220T grade.
3. What are the different types of Coils?
|
Copper coils can be classified into two: Soft and Rigid copper. No doubt, the copper coils have to pass through a heating and cooling process, making it hard. However, the process of annealing is repeated to make the material soft again. This type of copper coil is very flexible and can be reshaped when installing. Copper coils can be connected through welding, soldering, or brazing methods. Soft copper is the best fit for flare connections and is often used for coolant lines and heat pumps.
Rigid coils are the other type of copper coils. They are often referred to as pipes and renowned for the use in water lines. The hardening the rigid copper passes through makes it very difficult to bend, except the heating process is carried out again to make it soft. After that, bending can be done. |
4. What are the differences between Copper Coils and Tubes?
|
The term copper coils and tubes can be used interchangeably. However, for marine engineers, the two terms have different meanings with measurements and dimensions. Some of the differences between copper coils and tubes are in:
|
5. How do you put in a Copper Coil?
When installing copper coils, there may be some tolerance gaps noticed between the coil and the fittings. Not to worry, you can make use of capillary fittings. Capillary fittings have socket-like ends attached to the areas where tolerance gaps are noticed to help close them up. Also, the cleaning process can create some gaps between the coils and fittings. To fix this, melt the solder on the surface of the material. The melting process births adhesion and cohesion, allowing a flow of the solder into the gap for closure.
The installation method is explained below:
STEP 1
You have to measure the desired length for the coils. This process should be carefully done because it could affect the proper joining of the materials.
STEP 2
Then, you have to clean the coil and fittings to be used. You could either use sandpaper or steel wool to do this. Afterward, add sufficient flux to the surface area of the material. The cleaning process will ensure dirt and dust are prevented from entering the capillary gap.
STEP 3
The next process is the heating of the solder. The solder is brought to be heated on the area of the capillary gap. Sometimes, the solder may take a longer time to melt, continue till it melts and ensure the whole area is covered with the melted solder.
STEP 4
The completion of the soldering process is followed by cooling. The heated solder is left to cool down completely until it solidifies and closes the capillary gap entirely.
STEP 5
After cooling is completed, you want to clean the area to prevent excessive material on the surface.
***When soldering, you have to avoid melting excessive solder into the capillary gap.
The installation method is explained below:
STEP 1
You have to measure the desired length for the coils. This process should be carefully done because it could affect the proper joining of the materials.
STEP 2
Then, you have to clean the coil and fittings to be used. You could either use sandpaper or steel wool to do this. Afterward, add sufficient flux to the surface area of the material. The cleaning process will ensure dirt and dust are prevented from entering the capillary gap.
STEP 3
The next process is the heating of the solder. The solder is brought to be heated on the area of the capillary gap. Sometimes, the solder may take a longer time to melt, continue till it melts and ensure the whole area is covered with the melted solder.
STEP 4
The completion of the soldering process is followed by cooling. The heated solder is left to cool down completely until it solidifies and closes the capillary gap entirely.
STEP 5
After cooling is completed, you want to clean the area to prevent excessive material on the surface.
***When soldering, you have to avoid melting excessive solder into the capillary gap.
6. How do you clean Copper Coils?
|
Cleaning copper coils should be done periodically to prevent clogging of dirt and other elements in the channel. For example, many homes with AC systems often experience malfunctioning of the appliance after a while. If you fall into that category, you can use a little soap and water to dust the coil. While doing this, you can add a dash of vinegar and distilled water to the surface while washing. After that, rinse thoroughly and see the wonders of this simple process.
|
COPPER COILS CATALOGUE